Mastering Hormones: A Focus on Testosterone
Table of Contents
I. Introduction
Hormones are the unsung heroes of our bodies, orchestrating a complex symphony that affects everything from our mood to our physical health. These biochemical messengers wield tremendous influence, shaping the way we feel, think, and function daily. In this comprehensive exploration, we will venture deep into the intricate world of hormones, with a particular emphasis on one of the most crucial among them—testosterone. This hormone, often associated with masculinity, not only defines many aspects of a man’s physical and emotional well-being but also plays a pivotal role in women’s health.
Unveiling the Power of Testosterone
Our journey begins by unraveling the enigma of testosterone. To truly appreciate its significance, we must comprehend its essence, functions, and far-reaching implications. Through this article, we will embark on a journey of discovery, uncovering the profound effects of testosterone on our bodies, minds, and overall quality of life.
A Glimpse into Hormone Harmony
Hormones don’t work in isolation. They form an intricate network, a symphony, where each hormone has its unique role and, more importantly, interplays with others to maintain balance. Testosterone, with its remarkable attributes, is both a soloist and a conductor in this grand orchestra of hormones. As we delve deeper into its multifaceted roles, we’ll also explore the interconnectedness of hormones and how they collectively shape our health.
Diet, Lifestyle, and the Hormone Equation
But hormones aren’t solely determined by genetics; our daily choices play a pivotal role. This brings us to the heart of our exploration: the profound influence of diet and lifestyle on hormone balance. We’ll navigate through the intricate landscape of nutrition, exercise, sleep, and stress management, uncovering how these elements can either bolster or disrupt the delicate hormonal equilibrium.
Intriguingly, this article is not just about identifying problems but also about presenting solutions. We will equip you with practical knowledge and strategies to optimize your hormone health naturally, harnessing the power of good nutrition, mindful living, and informed choices.
So, let’s embark on this illuminating journey into the world of hormones, with testosterone as our guiding star, to unravel the mysteries, debunk the myths, and empower you with the tools to achieve hormonal harmony. Whether you’re a man seeking to enhance your vitality or a woman interested in understanding the intricate dance of hormones within your body, this comprehensive guide will provide invaluable insights into the fascinating realm of hormone health.
II. Testosterone: Understanding the Hormone
II.A What Is Testosterone?
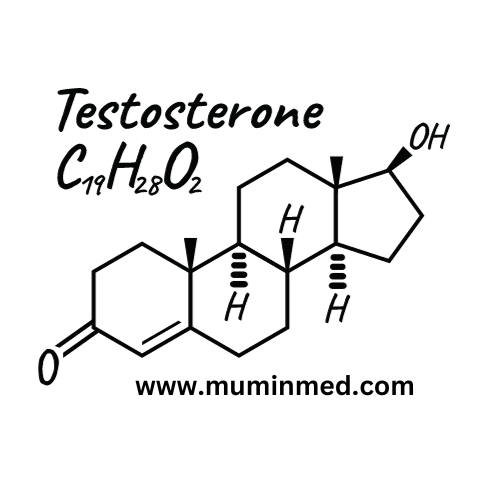
At the heart of our exploration lies the fascinating hormone known as testosterone. To understand its profound effects on our health, we must first grasp its fundamental nature. Testosterone, scientifically classified as a steroid hormone, belongs to a class of androgens primarily associated with male characteristics. However, it’s essential to note that testosterone isn’t exclusive to men; women also produce and rely on this hormone, albeit in smaller quantities.
Testosterone is produced primarily in the testes in men and the ovaries in women. A small amount is also synthesized in the adrenal glands. This hormone serves as a potent messenger within our bodies, affecting numerous physiological processes. It’s involved in the development of male sexual characteristics during puberty, such as the deepening of the voice, facial and body hair growth, and the growth of the Adam’s apple.
II.B The Role of Testosterone in Men’s Health
Beyond its role in shaping external physical traits, testosterone exerts a profound influence on several critical aspects of men’s health:
1. Muscle Mass and Strength: Testosterone is the driving force behind muscle growth and strength development in men. It stimulates the production of muscle protein, enabling the body to build and repair muscle tissue efficiently.
2. Bone Density and Health: Low testosterone levels can lead to decreased bone density, increasing the risk of fractures and conditions like osteoporosis. Maintaining adequate testosterone levels is crucial for preserving bone health.
3. Mood and Cognitive Function: While often associated with physical attributes, testosterone also plays a significant role in mood regulation and cognitive function. Low testosterone levels can contribute to mood swings, irritability, and difficulties with memory and concentration.
4. Libido and Sexual Function: Perhaps most famously, testosterone fuels the fires of desire and maintains healthy sexual function in men. It plays a pivotal role in maintaining erectile function, sperm production, and overall sexual well-being.
II.C Age-Related Testosterone Decline: Myth or Reality?
A prevailing belief suggests that testosterone levels inevitably decline with age, leading to a variety of health concerns. However, the reality is more complex. While it’s true that testosterone levels tend to decrease gradually as men age, this decline isn’t universal or necessarily problematic.
Testosterone levels can vary widely among individuals. Some men may experience a substantial drop in testosterone, while others maintain relatively stable levels throughout their lives. The decline in testosterone can be influenced by various factors, including genetics, lifestyle, and overall health.
Moreover, age-related changes in testosterone levels don’t always translate into negative health outcomes. Many older men maintain good physical and mental health despite lower testosterone levels. It’s essential to approach the topic of age-related testosterone decline with nuance, recognizing that individual experiences may differ significantly.
In the subsequent sections of this article, we’ll delve into the factors that can impact testosterone levels and explore practical ways to promote and maintain optimal hormone balance, regardless of age or gender.
III. Foods That Impact Hormone Health
III.A The Link Between Nutrition and Hormones
Understanding the intricate relationship between nutrition and hormones is fundamental to achieving hormonal balance and overall well-being. The foods we consume play a pivotal role in influencing the production, regulation, and function of hormones in our bodies. In this section, we will explore how nutrition impacts hormone health and delve into dietary choices that promote hormonal balance.
1. Macronutrients and Hormone Regulation:
a. Protein:
- Role: Protein is essential for the production of hormones and enzymes that regulate various bodily functions.
- Sources: Include lean meats, poultry, fish, dairy products, eggs, legumes, and plant-based protein sources like tofu and tempeh in your diet.
- Balancing Act: Opt for a variety of protein sources to ensure you receive a full spectrum of essential amino acids.
b. Carbohydrates:
- Role: Carbohydrates provide the body with energy, which is crucial for hormonal balance. However, the type and quality of carbohydrates matter.
- Sources: Choose complex carbohydrates like whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes over refined carbohydrates to stabilize blood sugar levels and support hormonal health.
c. Healthy Fats:
- Role: Dietary fats are precursors to hormones and play a vital role in hormone synthesis.
- Sources: Include sources of healthy fats such as avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish (e.g., salmon) in your diet. Omega-3 fatty acids, in particular, are known for their positive impact on hormone balance.
2. Micronutrients and Hormone Regulation:
a. Vitamins:
- Vitamin D: As previously discussed, vitamin D is essential for testosterone production. Ensure you receive adequate sunlight exposure or consider vitamin D supplements, especially if you have limited access to sunlight.
b. Minerals:
- Zinc: Zinc is a vital mineral for testosterone production. Dietary sources include oysters, beef, nuts, and seeds.
- Selenium: Selenium is important for thyroid hormone regulation. It can be found in foods like Brazil nuts, fish, and poultry.
- Magnesium: Magnesium plays a role in insulin sensitivity and may indirectly impact hormone balance. Leafy greens, nuts, and whole grains are good sources of magnesium.
3. The Impact of Sugar and Processed Foods:
- High Sugar Intake: Consuming excessive sugar, especially refined sugars and high-fructose corn syrup, can lead to insulin resistance and hormonal imbalances. Limiting sugar intake is essential for maintaining steady blood sugar levels.
- Processed Foods: Processed foods often contain trans fats, excess salt, and artificial additives, all of which can negatively impact hormone health. Minimize processed food consumption and focus on whole, unprocessed foods.
4. The Role of Fiber:
- Dietary Fiber: Fiber-rich foods, such as whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables, can aid in regulating insulin levels and promoting a feeling of fullness, preventing overeating and weight gain. A diet high in fiber supports hormonal balance.
5. Hydration Matters:
- Water: Staying well-hydrated is crucial for overall health and hormonal balance. Dehydration can lead to stress on the body and potentially affect hormone regulation.
6. Timing and Meal Composition:
- Meal Timing: Consistent meal timing can help regulate insulin and other hormones. Aim for regular meals and avoid long periods of fasting or irregular eating patterns.
- Balanced Meals: Include a balance of macronutrients (protein, carbohydrates, and fats) in each meal to provide a steady source of energy and support hormone production.
7. Individualized Nutrition:
- Bioindividuality: It’s important to recognize that nutritional needs can vary among individuals based on factors such as age, gender, genetics, and activity levels. Customizing your diet to your unique requirements can have a significant impact on your hormonal health.
In summary, the foods you choose to include in your diet have a profound influence on your hormone health. By prioritizing a diet rich in nutrient-dense whole foods, minimizing sugar and processed food intake, and staying well-hydrated, you can create a solid foundation for hormonal balance.
In the following section, we will explore the significance of hormone-friendly habits, including maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding environmental toxins, and practicing stress management, as crucial components of natural hormone optimization.
III.B Testosterone-Boosting Foods
When it comes to optimizing testosterone levels naturally, your dietary choices play a pivotal role. Incorporating specific testosterone-boosting foods into your diet can help support hormone production and balance. In this section, we will explore a selection of foods that have been shown to have a positive impact on testosterone levels.
1. Lean Proteins:
- Role: Protein is a key component in the production of hormones, including testosterone.
- Sources: Include lean protein sources in your diet such as chicken, turkey, lean beef, fish, and plant-based options like tofu and tempeh.
- Balanced Intake: Aim to distribute your protein intake evenly throughout the day to provide a steady supply of amino acids for hormone production.
2. Fatty Fish:
- Role: Fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which support hormone balance and overall health.
- Sources: Incorporate fatty fish into your diet at least twice a week to reap the benefits of their omega-3 content.
3. Nuts and Seeds:
- Role: Nuts and seeds are excellent sources of healthy fats, including monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats that are essential for hormone synthesis.
- Sources: Almonds, walnuts, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and pumpkin seeds are nutritious options to include in your diet.
4. Eggs:
- Role: Eggs are rich in cholesterol, which is a precursor to testosterone production. They also contain various vitamins and minerals essential for hormonal balance.
- Sources: Enjoy eggs as part of a balanced diet, but be mindful of overall cholesterol intake if you have specific dietary restrictions.
5. Cruciferous Vegetables:
- Role: Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts contain compounds that may help regulate estrogen levels in the body, indirectly supporting testosterone balance.
- Sources: Include these vegetables as part of your daily meals to harness their health benefits.
6. Garlic:
- Role: Garlic contains allicin, a compound that has been linked to increased testosterone levels and improved circulation.
- Sources: Add fresh garlic to your recipes or consider garlic supplements for potential benefits.
7. Pomegranates:
- Role: Pomegranates are rich in antioxidants, particularly ellagic acid, which may help reduce oxidative stress and support overall hormonal health.
- Sources: Enjoy fresh pomegranate seeds or opt for pomegranate juice without added sugars.
8. Spinach:
- Role: Spinach is a nutrient-dense leafy green that provides vitamins and minerals, including magnesium and vitamin B6, which are important for testosterone production.
- Sources: Incorporate spinach into salads, smoothies, or cooked dishes to boost your nutrient intake.
9. Ginger:
- Role: Ginger has been associated with increased testosterone levels and improved sperm quality in some studies.
- Sources: Include fresh or powdered ginger in your recipes, teas, or smoothies for potential benefits.
10. Oysters:
- Role: Oysters are exceptionally rich in zinc, a mineral crucial for testosterone production.
- Sources: Enjoy oysters as a seafood delicacy, or consider other zinc-rich foods like beef, pumpkin seeds, and lentils.
11. Berries:
- Role: Berries are packed with antioxidants that help reduce oxidative stress, potentially benefiting hormone balance.
- Sources: Blueberries, strawberries, raspberries, and blackberries are all excellent choices to incorporate into your diet.
12. Olive Oil:
- Role: Extra virgin olive oil contains monounsaturated fats, which can support hormone health and reduce inflammation.
- Sources: Use olive oil as a primary cooking oil or drizzle it over salads and vegetables.
13. Watermelon:
- Role: Watermelon contains citrulline, an amino acid that may have a positive impact on blood flow and, consequently, erectile function.
- Sources: Enjoy fresh watermelon as a delicious and hydrating summer snack.
14. Avocado:
- Role: Avocado is a source of healthy fats, fiber, and potassium, which can promote overall cardiovascular health and indirectly support hormone balance.
- Sources: Incorporate avocados into salads, sandwiches, or as a creamy addition to various dishes.
15. Brazil Nuts:
- Role: Brazil nuts are exceptionally rich in selenium, a mineral that supports thyroid function and overall hormonal health.
- Sources: Enjoy Brazil nuts as a snack or sprinkle chopped nuts over yogurt or oatmeal.
16. Cabbage:
- Role: Cabbage, like other cruciferous vegetables, contains compounds that may help regulate estrogen levels in the body.
- Sources: Include cabbage in salads, coleslaw, or stir-fry dishes for a hormone-friendly addition.
17. Tuna:
- Role: Tuna is not only a lean protein source but also contains vitamin D, which is essential for testosterone production.
- Sources: Enjoy canned tuna in salads, sandwiches, or as part of sushi rolls.
18. Red Grapes:
- Role: Red grapes contain resveratrol, an antioxidant that may support cardiovascular health and indirectly benefit hormone balance.
- Sources: Snack on red grapes or enjoy a glass of red wine (in moderation) for potential resveratrol benefits.
Incorporating these testosterone-boosting foods into your diet, along with maintaining a balanced and varied intake of macronutrients and micronutrients, can contribute to better hormonal health. Remember that a diverse and nutrient-rich diet, coupled with other lifestyle factors, forms the cornerstone of natural hormone optimization.
III.C Foods to Avoid for Hormone Balance
Just as certain foods can positively influence hormone health, others have the potential to disrupt hormonal balance. To maintain optimal hormonal well-being, it’s important to be aware of foods that may negatively impact hormone regulation. In this section, we will explore the foods to limit or avoid in your diet for better hormone balance.
1. Excessive Sugar and Refined Carbohydrates:
- Impact: High sugar intake and refined carbohydrates can lead to spikes and crashes in blood sugar levels. This can contribute to insulin resistance, a condition associated with hormonal imbalances, including elevated insulin and lower testosterone levels.
- Examples: Sugary beverages, candy, pastries, white bread, and sugary cereals.
- Recommendation: Limit the consumption of sugary and highly processed foods, opting for complex carbohydrates and natural sweeteners in moderation.
2. Processed and Fast Foods:
- Impact: Processed and fast foods are often high in unhealthy trans fats, excessive salt, and artificial additives. These components can disrupt hormone balance, increase inflammation, and negatively affect overall health.
- Examples: Fast food burgers, deep-fried items, packaged snacks, and microwave meals.
- Recommendation: Minimize the consumption of processed and fast foods, prioritizing fresh, whole foods instead.
3. Excessive Caffeine:
- Impact: While moderate caffeine intake is generally safe for most individuals, excessive caffeine consumption can lead to elevated cortisol levels, potentially disrupting hormone balance.
- Examples: High-caffeine energy drinks, multiple cups of strong coffee, and excessive caffeinated beverages.
- Recommendation: Enjoy caffeine in moderation, and consider switching to decaffeinated options later in the day to support better sleep.
4. Alcohol:
- Impact: Alcohol can have various effects on hormone balance. While moderate alcohol consumption may not significantly impact hormones, excessive and chronic alcohol use can lead to hormonal imbalances and liver damage.
- Examples: Frequent and heavy drinking.
- Recommendation: If you choose to consume alcohol, do so in moderation and be mindful of its potential effects on hormonal health.
5. Soy Products (in Excess):
- Impact: Soy contains phytoestrogens, which are plant compounds that can mimic the effects of estrogen in the body. While moderate soy consumption is generally safe, excessive soy intake, especially in men, may have unintended hormonal effects.
- Examples: Overconsumption of soy-based products like soy milk, tofu, or soy protein supplements.
- Recommendation: Include soy products in moderation as part of a balanced diet. For individuals concerned about the potential hormonal effects of soy, consult with a healthcare provider.
6. High-Sodium Foods:
- Impact: High-sodium diets can lead to elevated blood pressure and affect hormonal balance, particularly the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.
- Examples: Salty snacks, canned soups, processed meats, and restaurant/fast-food meals with high sodium content.
- Recommendation: Choose lower-sodium alternatives and limit the use of excessive salt in cooking.
7. Dairy Products with Added Hormones:
- Impact: Some conventional dairy products may contain added hormones, such as recombinant bovine growth hormone (rBGH). These hormones may indirectly affect human hormone levels.
- Examples: Conventional milk, cheese, and yogurt from cows treated with rBGH.
- Recommendation: Opt for organic and hormone-free dairy products when possible.
8. High-Mercury Fish:
- Impact: Certain fish, particularly large predatory species, can accumulate high levels of mercury. Excessive mercury consumption can disrupt hormonal balance and pose health risks, especially for pregnant women.
- Examples: Shark, swordfish, king mackerel, and tilefish.
- Recommendation: Choose fish lower in mercury, such as salmon, sardines, and trout, for a safer seafood option.
9. Non-Organic Produce with Pesticide Residues:
- Impact: Pesticide residues on non-organic produce may have endocrine-disrupting properties and interfere with hormone balance.
- Examples: Conventionally grown fruits and vegetables with known high pesticide residues.
- Recommendation: Consider choosing organic produce, especially for fruits and vegetables that are commonly treated with pesticides.
10. Artificial Sweeteners:
- Impact: While artificial sweeteners are calorie-free, some studies suggest they may disrupt hormonal signaling related to appetite and metabolism.
- Examples: Aspartame (Equal), sucralose (Splenda), saccharin (Sweet’N Low), and acesulfame potassium (Ace-K).
- Recommendation: Limit the use of artificial sweeteners and explore natural alternatives like stevia or monk fruit.
By being mindful of these foods and their potential impacts on hormone balance, you can make informed dietary choices that support your overall health and well-being. Remember that moderation and a balanced, nutrient-dense diet are key to maintaining hormonal harmony.
IV. Lifestyle Factors: Balancing the Hormone Equation
IV.A Sleep: The Unsung Hero of Hormone Health
While dietary choices significantly impact hormone balance, they are just one piece of the puzzle. Adequate sleep, often underestimated, plays a pivotal role in nurturing hormonal harmony. Sleep is a dynamic process during which hormones are released, regulated, and reset. Let’s delve into the profound connection between sleep and testosterone, along with practical tips to enhance your sleep quality.
Quality sleep is the foundation of hormonal health. During deep sleep, the body initiates essential processes related to hormone production, including the release of growth hormone, which is closely linked to testosterone. Sleep deprivation, on the other hand, disrupts these processes, leading to imbalances in hormones, including a decrease in testosterone.
Tips for Improving Sleep Quality:
- Establish a consistent sleep schedule.
- Create a conducive sleep environment by keeping the room dark, quiet, and cool.
- Limit exposure to screens before bedtime, as the blue light emitted by electronic devices can interfere with the production of melatonin, a hormone crucial for sleep.
- Practice relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation, to reduce stress and ease into sleep.
IV.B Stress Management: The Hormone Killer
Stress is an omnipresent force in our lives, and its impact on hormone health cannot be overstated. One of the primary hormones affected by stress is cortisol, often referred to as the stress hormone. Cortisol and testosterone share an inverse relationship, meaning that when cortisol levels are high due to chronic stress, testosterone levels tend to decline.
Techniques for Stress Reduction:
- Engage in regular physical activity, which can help reduce stress and support hormone balance.
- Incorporate relaxation practices like yoga or mindfulness meditation into your daily routine.
- Prioritize time for hobbies and activities that bring joy and relaxation.
- Seek support from friends, family, or a therapist when dealing with chronic stress.
IV.C Exercise: The Powerhouse of Hormone Optimization
Exercise is a potent tool for maintaining hormonal health. It not only contributes to overall well-being but also has a direct impact on testosterone levels. Understanding the types of exercise and their effects on hormones is essential for harnessing their benefits.
Strength Training vs. Cardiovascular Exercise:
- Strength Training: Resistance exercises, such as weightlifting, increase muscle mass and stimulate testosterone production. Compound movements like squats and deadlifts are particularly effective for boosting testosterone levels.
- Cardiovascular Exercise: While cardio is essential for heart health, excessive endurance training, such as long-distance running, can temporarily lower testosterone levels. However, moderate-intensity cardiovascular workouts have a positive overall impact on hormone balance.
Creating an Effective Exercise Routine:
- Balance your exercise routine by incorporating both strength training and cardiovascular workouts.
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week, along with muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days per week.
By paying attention to your sleep patterns, stress management, and exercise regimen, you can take proactive steps to optimize your hormone health naturally. These lifestyle factors are within your control and can contribute significantly to achieving and maintaining hormonal harmony. In the subsequent sections, we’ll explore additional natural approaches to boost testosterone and dispel common myths surrounding this essential hormone.
V. Natural Ways to Boost Testosterone
In our pursuit of optimizing testosterone levels naturally, it’s crucial to explore a variety of approaches that align with a holistic and sustainable approach to health. By focusing on lifestyle modifications, dietary choices, and hormonal-friendly habits, individuals can influence their hormonal balance positively. In this section, we will delve into these natural methods for boosting testosterone levels.
V.A The Role of Supplements
While a balanced diet is essential for overall health, certain supplements can complement your efforts to support hormonal balance. These supplements contain key nutrients and compounds known to have a positive impact on testosterone levels:
1. Vitamin D:
- Role: Vitamin D is often referred to as the “sunshine vitamin” because the body produces it in response to sunlight exposure. It plays a crucial role in testosterone production.
- Sources: Sunlight, fatty fish (e.g., salmon, mackerel), fortified foods, and supplements.
- Recommended Intake: Consult with a healthcare provider to determine your specific needs.
2. Omega-3 Fatty Acids:
- Role: Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish like salmon and flaxseeds, have been shown to support hormone balance and reduce inflammation.
- Sources: Fatty fish, flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, and fish oil supplements.
- Recommended Intake: Aim for at least two servings of fatty fish per week or consider supplementation if necessary.
3. Herbal Supplements:
- Fenugreek: Fenugreek is an herb known for its potential to boost testosterone levels and may also improve libido.
- Ashwagandha: As an adaptogenic herb, ashwagandha can reduce stress and support overall hormonal balance.
- Tribulus Terrestris: This herb has been used traditionally to enhance testosterone levels, although scientific evidence is mixed.
It’s important to note that while supplements can be valuable additions to your regimen, they should be used judiciously and under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Nutrient needs vary among individuals, and excessive supplementation can have adverse effects.
V.B Hormone-Friendly Habits
The journey to optimizing testosterone levels naturally extends beyond supplements and diet. Incorporating hormone-friendly habits into your daily life is equally critical:
1. Maintaining a Healthy Weight:
- Excess body fat, especially around the abdominal area, can contribute to hormonal imbalances, including elevated estrogen levels. Shedding excess weight through a combination of diet and exercise can lead to improvements in hormonal health.
2. Avoiding Toxins:
- Environmental toxins, such as those found in plastics, pesticides, and certain personal care products, can disrupt the hormone balance. Minimize exposure to these toxins by opting for natural and eco-friendly products whenever possible.
3. Stress Management:
- Chronic stress can significantly impact hormone balance, leading to increased cortisol levels and reduced testosterone levels. Practicing stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga can help lower cortisol levels and support overall hormone balance.
V.C The Importance of Sleep
One of the most underrated factors in maintaining hormonal health is the quality and duration of sleep. Sleep is not merely a period of rest; it’s a dynamic process during which hormones are released, regulated, and reset. Here’s why sleep matters for testosterone:
Role of Sleep in Hormone Production:
- During deep sleep, the body initiates essential processes related to hormone production, including the release of growth hormone, which is closely linked to testosterone.
- Sleep deprivation disrupts these processes, leading to imbalances in hormones, including a decrease in testosterone.
Tips for Improving Sleep Quality:
- Establish a Consistent Sleep Schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends.
- Create a Conducive Sleep Environment: Keep the bedroom dark, quiet, and cool for optimal sleep conditions.
- Limit Screen Time Before Bed: Exposure to the blue light emitted by electronic devices can interfere with the production of melatonin, a hormone crucial for sleep. Avoid screens at least an hour before bedtime.
- Practice Relaxation Techniques: Engage in relaxation practices such as deep breathing or meditation to reduce stress and ease into sleep.
By paying attention to your sleep patterns and implementing strategies to improve sleep quality, you can take proactive steps toward optimizing your hormone health naturally.
V.D The Exercise Factor
Exercise is a potent tool for maintaining hormonal health, particularly testosterone levels. Understanding the types of exercise and their effects on hormones is essential for harnessing their benefits.
1. Strength Training vs. Cardiovascular Exercise:
- Strength Training: Resistance exercises, such as weightlifting, increase muscle mass and stimulate testosterone production. Compound movements like squats and deadlifts are particularly effective for boosting testosterone levels.
- Cardiovascular Exercise: While cardio is essential for heart health, excessive endurance training, such as long-distance running, can temporarily lower testosterone levels. However, moderate-intensity cardiovascular workouts have a positive overall impact on hormone balance.
Creating an Effective Exercise Routine:
- Balanced Exercise: Incorporate both strength training and cardiovascular workouts into your exercise routine.
- Aerobic Activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week, along with muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days per week.
V.E Summary of Natural Approaches to Boost Testosterone:
In summary, optimizing testosterone levels naturally involves a multi-faceted approach that includes dietary choices, lifestyle modifications, and hormonal-friendly habits. By paying attention to what you eat, how you exercise, the quality of your sleep, and your overall stress management, you can positively influence your hormone health.
It’s important to remember that achieving and maintaining hormonal balance is a journey that requires consistency and patience. These natural approaches can complement each other and contribute to a healthier, more balanced life.
In the subsequent sections, we will address additional topics related to testosterone, including common myths and misconceptions, and the importance of informed decision-making when it comes to hormone health.
VI. Testosterone Myths and Misconceptions
Myths and misconceptions about testosterone abound, often fueled by incomplete information, stereotypes, and sensationalism. In this section, we will delve into some of the most persistent myths surrounding testosterone and clarify the facts to promote a better understanding of this essential hormone.
VI.A Busting Common Myths About Testosterone
1. Testosterone and Aggression:
Myth: Testosterone is synonymous with aggression, leading to violent and aggressive behavior in men.
Fact: The relationship between testosterone and aggression is far more complex than the myth suggests. While testosterone does play a role in influencing behavior, it is not the sole determinant of aggression. Aggressive behavior is influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors.
Research has shown that high testosterone levels alone do not lead to aggression, but rather, they can amplify preexisting tendencies. Testosterone has been linked to both prosocial and aggressive behaviors, depending on the individual’s context and personality.
2. Testosterone and Hair Loss:
Myth: High testosterone levels cause male pattern baldness.
Fact: Male pattern baldness, or androgenetic alopecia, is primarily determined by genetic factors and hormonal interactions, particularly with dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a derivative of testosterone. While genetics plays a significant role, high levels of DHT can lead to hair follicle miniaturization and eventual hair loss in individuals predisposed to male pattern baldness.
It’s important to note that many men with high testosterone levels do not experience hair loss, and conversely, some with low testosterone levels may still develop male pattern baldness. Hair loss is a complex condition influenced by multiple factors.
3. Testosterone and Heart Health:
Myth: Higher testosterone levels are associated with an increased risk of heart disease.
Fact: The relationship between testosterone and heart health is multifaceted and not fully understood. Some studies have suggested that low testosterone levels may be associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. However, the connection is not straightforward, as other factors like age, lifestyle, and underlying health conditions play significant roles.
It’s essential to recognize that the impact of testosterone on heart health varies among individuals, and the overall picture is more nuanced than a simple association between testosterone levels and heart disease.
VI.B Recognizing the Dangers of Steroid Abuse
While we’ve addressed common misconceptions about testosterone, it’s equally crucial to recognize the dangers of anabolic steroid misuse. Anabolic steroids are synthetic versions of testosterone that are often abused to enhance athletic performance and muscle growth.
Dangers of Anabolic Steroid Abuse:
- Physical Health Risks: Prolonged use of anabolic steroids can lead to a range of adverse health effects, including liver damage, cardiovascular problems, and high blood pressure.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Abuse of steroids can disrupt the body’s natural hormone production, leading to imbalances that can have long-lasting consequences, including testicular atrophy and fertility issues.
- Psychological Effects: Steroid abuse can lead to mood swings, aggression, and psychiatric disorders, such as “roid rage.”
- Legal and Ethical Concerns: The non-medical use of anabolic steroids is illegal in many countries and is prohibited by most sports organizations due to ethical concerns and unfair competitive advantages.
In summary, while testosterone myths persist, it’s crucial to approach the subject with a nuanced understanding of the hormone’s role and the potential consequences of its misuse. Promoting accurate information about testosterone and discouraging steroid abuse is essential for the well-being of individuals and the integrity of sports and competition.
VII. Empowering Yourself with Knowledge
As we conclude this comprehensive exploration into the world of hormones, particularly the role of testosterone, it’s important to recognize the transformative power of knowledge. Armed with a deeper understanding of hormones and the practical strategies presented throughout this article, you have the tools to take charge of your health and well-being.
Knowledge as a Catalyst for Change
- Informed Decision-Making: Understanding the intricate web of hormones and their impact on your health empowers you to make informed decisions about your lifestyle, diet, and healthcare. Rather than relying on myths or hearsay, you can make choices grounded in scientific understanding.
- Proactive Health Management: With knowledge comes the ability to proactively manage your health. You can adopt hormone-friendly habits, such as maintaining a healthy diet, managing stress, getting regular exercise, and ensuring sufficient sleep. These lifestyle choices contribute to hormonal balance and overall well-being.
- Effective Communication: Armed with knowledge, you can engage in more meaningful and productive conversations with healthcare professionals. When discussing concerns or seeking guidance, your understanding of hormones and their roles allows for more precise communication and better-informed decisions about your health.
The Journey Towards Hormonal Harmony
- Personalized Approaches: Recognizing that hormone health is not a one-size-fits-all endeavor, you can tailor your approach to your unique needs and circumstances. Factors such as age, gender, genetics, and lifestyle all play a role in hormone balance. Your knowledge allows you to personalize your strategies accordingly.
- Long-Term Wellness: The pursuit of hormonal harmony is not a short-term fix but a lifelong journey. By embracing the principles discussed in this article, you can lay the foundation for sustained well-being throughout your life.
Advocacy and Education
- Spreading Accurate Information: With your newfound knowledge, you can become an advocate for hormone health within your community, dispelling myths and promoting evidence-based understanding. Educating others about the importance of hormonal balance and responsible practices is a valuable contribution to public health.
- Supporting Others: If you encounter friends, family members, or peers struggling with hormone-related issues, you can offer support and share the knowledge you’ve acquired. Empowering others to take control of their health can have a positive ripple effect on individuals and communities.
Conclusion
As you embark on your journey towards hormone health, remember that knowledge is the most potent tool at your disposal. By understanding the intricacies of hormones, particularly the role of testosterone, and by embracing lifestyle choices that support hormonal balance, you can empower yourself to lead a healthier, more balanced life.
Ultimately, the pursuit of hormone health is a lifelong commitment, one that involves ongoing education, self-awareness, and a dedication to making informed choices. With the knowledge gained from this article, you are better equipped to navigate the complexities of hormones and take proactive steps toward a more vibrant and fulfilling life.
VIII. FAQs
- What is the normal range of testosterone levels in men and women?
- Testosterone levels can vary, but for adult men, the normal range is typically between 270 to 1070 ng/dL (nanograms per deciliter), while for adult women, it’s about 15 to 70 ng/dL.
- What are the common signs of high testosterone levels in men and women?
- High testosterone levels can lead to symptoms like acne, increased facial and body hair growth, mood swings, and menstrual irregularities in women.
- Can lifestyle changes alone significantly raise testosterone levels?
- Yes, lifestyle changes, including dietary improvements, exercise, stress management, and better sleep, can lead to noticeable increases in testosterone levels for some individuals.
- Is testosterone therapy safe, and what are its potential side effects?
- Testosterone therapy can be safe when prescribed and monitored by a healthcare professional. However, it may have side effects, including mood swings, changes in blood pressure, and potential effects on the prostate.
- Can women benefit from testosterone therapy, and if so, in what circumstances?
- Yes, some women with certain medical conditions like low libido and menopausal symptoms may benefit from testosterone therapy. It should only be considered under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
- How long does it take to see noticeable changes in testosterone levels with lifestyle modifications?
- The time it takes to see changes in testosterone levels can vary from person to person. Some individuals may notice improvements in a matter of weeks, while others may take several months of consistent efforts.
- Are there natural ways to address hormone imbalances in women during menopause?
- Yes, lifestyle adjustments, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress reduction, and hormone-friendly supplements, can help women manage hormone imbalances during menopause.
- Can testosterone levels be too high, and what are the risks associated with excessive testosterone?
- Extremely high testosterone levels, often caused by medical conditions, can have adverse effects on health, including mood disturbances, cardiovascular issues, and fertility problems.
- Are there specific exercises that are more effective at boosting testosterone levels in men?
- Compound strength-training exercises like squats, deadlifts, and bench presses are particularly effective at increasing testosterone levels in men.
- Can hormonal imbalances be a factor in unexplained weight gain?
- Yes, hormonal imbalances, including imbalances in insulin, cortisol, and sex hormones like testosterone, can contribute to unexplained weight gain in both men and women.
IX. Additional Resources and References
Books:
- “The Hormone Cure: Reclaim Balance, Sleep, Sex Drive, and Vitality Naturally with the Gottfried Protocol” by Sara Gottfried, MD.
- “Testosterone: A Man’s Guide: Practical Tips for Boosting Physical, Mental, and Sexual Vitality” by Nelson Vergel.
- “The Testosterone Optimization Therapy Bible: The Ultimate Guide to Living a Fully Optimized Life” by Jay Campbell and Jim Brown.
Websites and Organizations:
- The Hormone Health Network – A resource provided by The Endocrine Society, offering information on various hormones, including testosterone.
- Mayo Clinic – Testosterone Therapy – Mayo Clinic’s overview of testosterone therapy, its uses, and potential risks.
- Harvard Health Publishing – Testosterone and Men’s Health – Articles and insights on testosterone from Harvard Medical School.
Research Papers and Articles:
- Traish, A. M., Miner, M. M., Morgentaler, A., Zitzmann, M. (2011). Testosterone deficiency. The American Journal of Medicine, 124(7), 578-587. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2010.12.017
- Isidori, A. M., Buvat, J., Corona, G., Goldstein, I., Jannini, E. A., Lenzi, A., & Porst, H. (2015). A critical analysis of the role of testosterone in erectile function: from pathophysiology to treatment—a systematic review. European Urology, 65(1), 99-112. DOI: 10.1016/j.eururo.2013.08.048
- Hackett, G., Cole, N., Bhartia, M., Kennedy, D., Raju, J., Wilkinson, P., … & Jones, T. H. (2017). The response to testosterone undecanoate in men with type 2 diabetes is dependent on achieving threshold serum levels (the BLAST study). International Journal of Clinical Practice, 71(9), e12977. DOI: 10.1111/ijcp.12977
- Rohrmann, S., Platz, E. A., Selvin, E., Shiels, M. S., Joshu, C. E., Menke, A., … & Sarma, A. V. (2011). The prevalence of low testosterone levels among men with type 2 diabetes: a nationally representative study. International Journal of Clinical Practice, 65(11), 1120-1129. DOI: 10.1111/j.1742-1241.2011.02798.x